The Mississippi Supreme Court handed down two opinions yesterday. The most interesting is technically an adoption case, but it involves jurisdictional issues, unwritten local chancery court rules, appellate procedure, and appellate remedies. Both the majority opinion and the partial concurrence/partial dissent are worth your time.
Wiggins v. Southern Securities Group, LLC, 2024-CA-00251-SCT (Civil – Contract)
Affirming the trial court’s decision in a contract/business dispute, holding that the trial court did not err in granting one side’s motion for preliminary injunction or in denying the other side’s motion to compel mediation and/or arbitration.
(8-1: Griffis for the Court; Coleman dissented)
In the Matter of L.L.T.: Prince v. Mississippi Department of Child Protection Services, 2024-IA-00824-SCT (Civil – Adoption)
Affirming the youth court’s ruling that it lacked jurisdiction to finalize an adoption against a backdrop of the chancery court refusing set a hearing on adoption petitions, holding that the youth court did not err in finding that it lacked jurisdiction since chancery courts have exclusive jurisdiction.
(5-4: Coleman for the Court; Randolph dissented, joined by Ishee, Griffis, and Branning)
Note – The procedural posture of this one is strange as a result of the chancery court refusing to set a hearing on adoption petitions. The petitioner got creative and initiated the youth court action to create a record for an appeal so that they could seek relief from the appellate courts. The youth court ruled that it lacked jurisdiction and the petitioner was able to appeal. On appeal, the majority of the Supreme Court agreed that the youth court lacked jurisdiction but held that they could not provide any relief other than to affirm the youth court because no other relief was specifically sought. The Supreme Court made it clear that the chancery court should act, but found that it lacked a mechanism based on the issue presented on appeal to compel the chancery court to act. Here is how the majority opinion concluded:
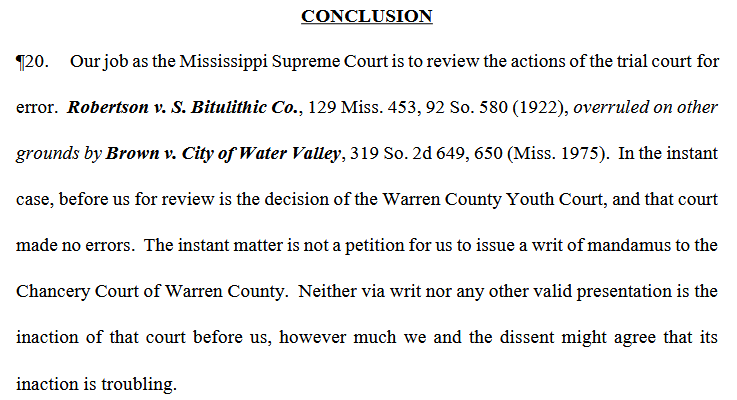
The partial concurrence/partial dissent agreed that the youth court lacked jurisdiction, but was less diplomatic about the chancery court’s conduct and disagreed that Supreme Court’s hands are tied on this appeal:

Other Orders
- McGee v. State, 2023-CT-00083-SCT (denying cert)
- Childs v. State, 2023-CT-00126-SCT (denying cert)
- In the Matter of Estate of Johnson: Manners v. Estate of Johnson, 2023-CT-00823-SCT (denying rehearing)
- McNaughton v. State, 2023-CT-01099-SCT (denying cert)
- Caffey v. Forrest Health, 2023-CT-01232-SCT (denying cert)
- Carr v. State, 2024-CT-00185-SCT (denying cert)
- Horne v. Dolgencorp LLC, 2024-CT-00376-SCT (denying cert)
- Strong v. Acara Solutions, Inc., 2024-CT-00455-SCT (granting cert)
- Rogers v. State, 2025-M-00257 (granting application for leave to proceed in the trial court)
