The Mississippi Court of Appeals handed down nine opinions today and one bonus opinion Thursday of last week. There are a few real property cases including a restrictive covenants case. There are two interesting speedy trial cases among several other direct criminal appeals.
February 13, 2025
Johnson v. Cleveland, 2023-CA-01011-COA (Civil – Real Property)
Reversing the chancery court’s decision in a tax sale and forfeited tax land patents, holding that a potential adverse possession claim did not confer standing, that the plaintiff lacked standing per section 29-1-21, and that the chancellor erred in declaring the tax sale void and ordering that the forfeited tax land patents be cancelled.
(6-4: Westbrooks dissented, joined by Barnes, McDonald, and Lawrence)
February 18, 2025
Wallace v. State, 2023-KA-00721-COA consolidated with 2023-KA-00723-COA, consolidated with 2023-KA-00888-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming convictions of three brothers who were tried together of capital murder, holding that the convictions were supported by sufficient evidence, that the trial court’s decision to allow an investigator to testify about a witness’s prior statement was harmless error, that the trial court did not in error for allowing testimony of prior bad acts to which there was no timely objection, that there was no violation of the constitutional right to a speedy trial under the totality of the circumstances, and that one brother’s ineffective assistance of counsel argument was without merit.
(7-3-0: Lawrence and McCarty concurred in part and in the result without writing; Westbrooks concurred in result only without writing)
Note – The speedy trial discussion is worth reading if that is in your wheelhouse.
1st Step Sober Living LLC v. Cleveland, 2023-CA-00665-COA (Civil – Other)
Affirming the chancellor’s decision granting residents’ request for injunctive relief preventing a home in a subdivision from being used by individuals recovering from substance abuse disorder, holding that the sale of the subject property did not render the case moot because damages were sought, that the proposed use was a commercial endeavor that was prohibited by restrictive covenants, and the chancellor did not err in determining that the rehab home did not sufficiently prove that the tenants would fit the “handicap” criteria for FHA purposes.
(10-0)
Brooks v. State, 2023-KA-01081-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of possession of a controlled substance and being a felon in possession of a firearm, holding that the evidence was sufficient to support both convictions.
(10-0)
Chambers v. State, 2023-KA-00626-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of one count of capital murder and two counts of felonious child abuse, holding that the trial court did not err in denying the defendant’s motion to suppress her statement to investigators where she voluntarily, knowingly, and intelligently waived her Miranda rights and that the State presented sufficient evidence for all convictions.
(9-1-0: Wilson concurred in part and in the result without writing)
LoanMax, LLC v. Castle Columbus I, LLC, 2023-CA-00790-COA (Civil – Contract)
Affirming in part and reversing in part the chancery court’s rulings in a claim for declaratory and injunctive relief involving a commercial lease renewal, holding on direct appeal that the chancellor did not err in finding that lessee did not provide notice required to effectively renew the lease, on cross-appeal that the chancellor did not err in finding that the owner is not entitled to damages for roofing or HVAC or to attorney’s fees, and on cross-appeal that the chancellor erred in her findings on holdover rent and remanded for a determination of what back rent may be owed.
(9-0: Barnes did not participate)
Taylor v. State, 2023-KA-00245-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of aggravated assault with a deadly weapon, holding that the defendant’s right to speedy trial was not violated.
(7-4*-0: McCarty specially concurred, joined by McDonald and St. Pe (who also joined the majority); Lawrence concurred in part and in the result without writing)
Note – The constitutional right to speedy trial got a lot of air time today. Here is how McCarty’s special concurrence on the subject kicks off:
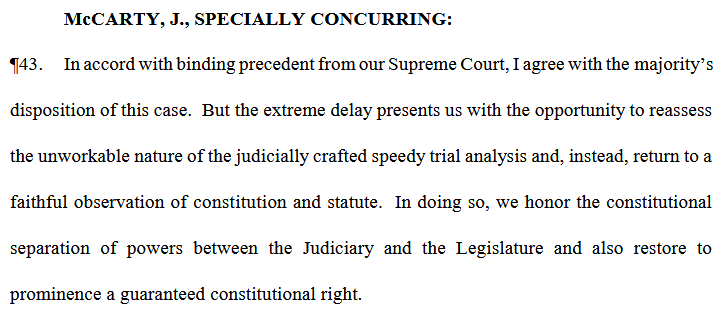
Spearman v. State, 2023-KA-01091-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of aggravated assault, holding that there were no arguable issues for appeal after reviewing counsel’s Lindsey brief and the record.
(10-0)
Fears v. State, 2023-KA-00174-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of capital murder, armed robbery, conspiracy to commit armed robbery, and aggravated assault against victims responding to a fake Facebook Marketplace ad, holding that the trial court did not abuse its discretion in denying an accomplice jury instruction.
(10-0)
Johnson v. State, 2023-KA-00369-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming convictions of capital murder and felony child abuse, holding that the defendant abandoned his motion to server the counts against him when he failed to pursue a motion to hearing a decision and, further, that the trial court did not abuse its discretion denying the motion to sever.
(10-0)
Other Orders
- Johnson v. SW Gaming, LLC, 2023-CA-00505-COA (denying rehearing)
- Simmons v. State, 2023-KA-00518-COA (denying rehearing)





