The Mississippi Court of Appeals handed down three opinions on Tuesday. The case that stood out to me was Murphy v. William Carey University not because of the result but because of how the Court of Appeals discussed the Horton doctrine. The special concurrence pulled no punches.
Frazier v. State, 2022-KA-00896-COA (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of first-degree murder with firearm enhancement, holding that the circuit court did not err in denying a heat-of-passion manslaughter instruction and did not abuse its discretion in refusing to allow the defendant to read proffered testimony from the first trial that ended with a mistrial on the first-degree murder charge.
(10-0)
Murphy v. William Carey University, 2022-CA-00379-COA (Civil – Med Mal)
Reversing the trial court’s grant of summary judgment in a med mal case based on lack of pre-suit notice and the statute of limitations, holding that the defendant waived those defenses by failing to pursue them while actively participating in litigation.
(7-2: Lawrence specially concurred joined by McDonald, Smith, and Emfinger, and joined in part by Wilson and Westbrooks; Greenlee dissented, joined by Carlton)
NOTE – I find the discussion of the Horton doctrine fascinating. The majority opinion and the special concurrence threw some shade at the development of the Horton doctrine and how it has been applied. The majority opinion included this statement and footnote:
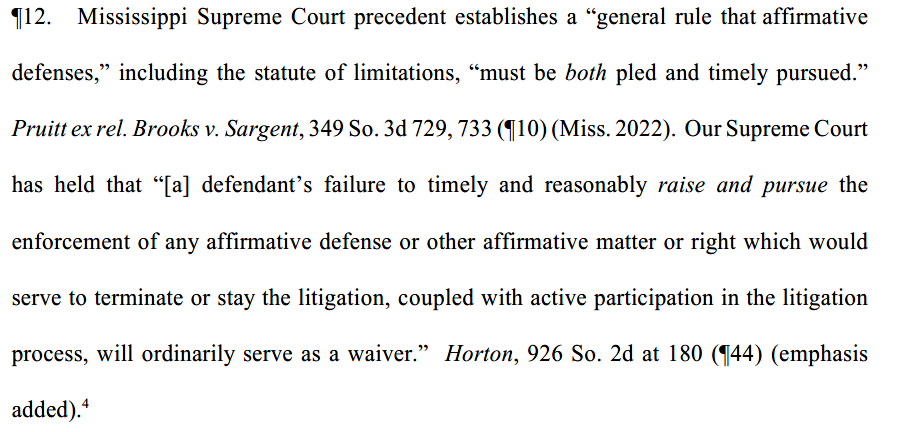

The special concurrence upped the ante and sharply criticized the state of the Horton doctrine. I read the special concurrence (carrying four votes and two “in part” votes) as a challenge to the Mississippi Supreme Court to clean up the Horton doctrine:


The special concurrence concluded with this:

I am not sure this is the best “test case” for the Horton doctrine based on the facts, but I will be watching for a cert petition.
The City of Pascagoula, Mississippi v. Cumbest, 2022-CA-00745-COA (Civil – State Boards & Agencies)
Reversing on direct appeal and reversing on cross-appeal in a case over whether private property was “menace” under Miss. Code Ann. section 21-19-11, holding that the circuit court erred in reversing the city council’s determination that the property was a “menace” and finding no abuse of discretion in the circuit court’s denial of the property owner’s decision denying the owner’s motion to compel production of documents.
(5-4: Westbrooks concurred in part and dissented in part without separate written opinion; McDonald concurred in part and dissented in part, joined by Wilson, Westbrooks, and McCarty; Lawrence did not participate)
NOTE – The concurrence took issue with the City making the “menace” determination based on the condition of the property before the hearing and not at the time of the hearing.
Other Orders
Friley v. State, 2021-KA-00791-COA (denying rehearing)
Smith v. Ford, 2022-CA-00255-COA (denying rehearing)
Burns v. BancorpSouth Bank, 2022-CA-00404-COA (denying rehearing)
Moore v. Mississippi Farm Bureau Casualty Insurance Company, 2022-CA-00555-COA (denying rehearing)
Edwards v. State, 2022-KA-00719-COA (recalling mandate and permitting pro se motion for rehearing to proceed)
Scales v. State, 2022-KA-00856-COA (denying rehearing)
Thompson v. Thompson, 2022-CA-01014-COA (dismissing motion for rehearing as untimely)




