The Mississippi Supreme Court handed down four opinions today. There was a UM dec action along with three direct criminal appeals. One of the direct criminal appeals resulted in reversal based on an erroneous jury instruction.
Williams v. Mississippi Farm Bureau Cas. Ins. Co., 2023-CA-01225-SCT (Civil – Insurance)
Affirming the trial court’s decision granting a UM carrier’s motion for summary judgment in a dec action, holding that the UM policy did not unlawfully restrict or reduce coverage mandated by Mississippi’s UM Act and that clear and unambiguous language in the policy excluded ATVs from the term “uninsured motorist.”
(9-0)
Barnett v. State, 2023-KA-00742-SCT (Criminal – Felony)
Reversing conviction for sale of meth, holding that the trial court committed reversible error by giving a jury instruction that improperly commented on the weight of the evidence.
(7-2: Randolph dissented, joined by Branning)
N0te – Here is the text of the jury instruction that warranted reversal:
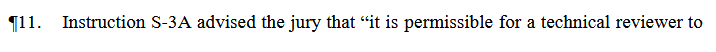

Robinson v. State, 2023-KA-00773-SCT (Criminal – Felony)
Affirming conviction of aggravated assault, holding that the evidence was sufficient to support the conviction, and rejecting the appellant’s pro se arguments that his appellate counsel were ineffective, that the State committed Brady violations, and that the trial court lacked jurisdiction.
(9-0)
Kendrick v. State, 2024-KM-00510-SCT (Criminal – Misdemeanor)
Affirming the circuit court’s decision affirming the county court’s decision affirming a municipal court conviction of DUI first offense and possession of drug paraphernalia, holding that the county court did not err in denying a motion to suppress that claimed the traffic stop was illegal.
(8-0: Randolph did not participate)
Other Orders
- In Re: The Rules of Civil Procedure, 89-R-99001-SCT (granting motion to amend M.R.C.P. 14 to be effective 30 days from the entry of the order on January 27, 2025)
- In Re: Weaver, 2017-M-00527 (denying misnamed application for leave to seek post-conviction relief in the trial court, finding the application successive and frivious, and warning that future frivolous filings may result in sanctions)
- Lestrick v. State, 2021-CT-01409-SCT (dismissing cert petition)
- Gilmer v. Biegel, 2022-CP-00528 (denying motion for citation of contempt and sanctions and ordering payment of sanction)
- Weatherly v. Weatherly, 2022-CT-00804-SCT (granting cert)
- Jackson v. State, 2023-CT-00201-SCT (denying cert)
- Jackson v. State, 2023-CT_201-SCT (denying pro se cert petition)
- Carpenter v. State, 2023-CT-00580-SCT (denying cert)CT (denying cert)
- In Re Validation of up to $27,600,000 Trust Certificates Evidencing Proportional Interests in a Lease by The Simpson County School District: Floyd v. Simpson County School Board, 2023-CA-01126-SCT (denying motion for rehearing and amended motion for rehearing)
- Parker v. Stewart, 2023-CA-01257-SCT (granting motion to dismiss appeal)
- Parker v. Stewart, 2023-CA-01257 (per curiam affirmance)



